Understanding Applied Science: Bridging Technology and Engineering for Real-World Solutions
Introduction: The Power of Applied Science
Applied science is a transformative approach that takes scientific discoveries out of the laboratory and puts them to work in the real world. By bridging the gap between pure research and practical application, applied science drives innovation, improves everyday life, and forms the backbone of modern technology and engineering. This article explores alternative terms for applied science, examines the science that combines technology and engineering, and provides comprehensive guidance for students and professionals interested in these dynamic fields.
What Is Another Term for Applied Science?
Applied science is commonly known by several alternative terms, depending on the context and field of application. Some of the most widely recognized synonyms and related concepts include:
- Practical science : Emphasizes the use of scientific principles to address real-world problems [2] .
- Engineering science : Focuses on applying scientific knowledge specifically within engineering disciplines [1] .
- Technology : While technology often refers to the tools and systems themselves, it also encompasses the applied processes that create them [3] .
In essence, applied science is an umbrella term that covers any field using scientific methods and knowledge to solve practical challenges, whether in healthcare, business, agriculture, or technology [5] .
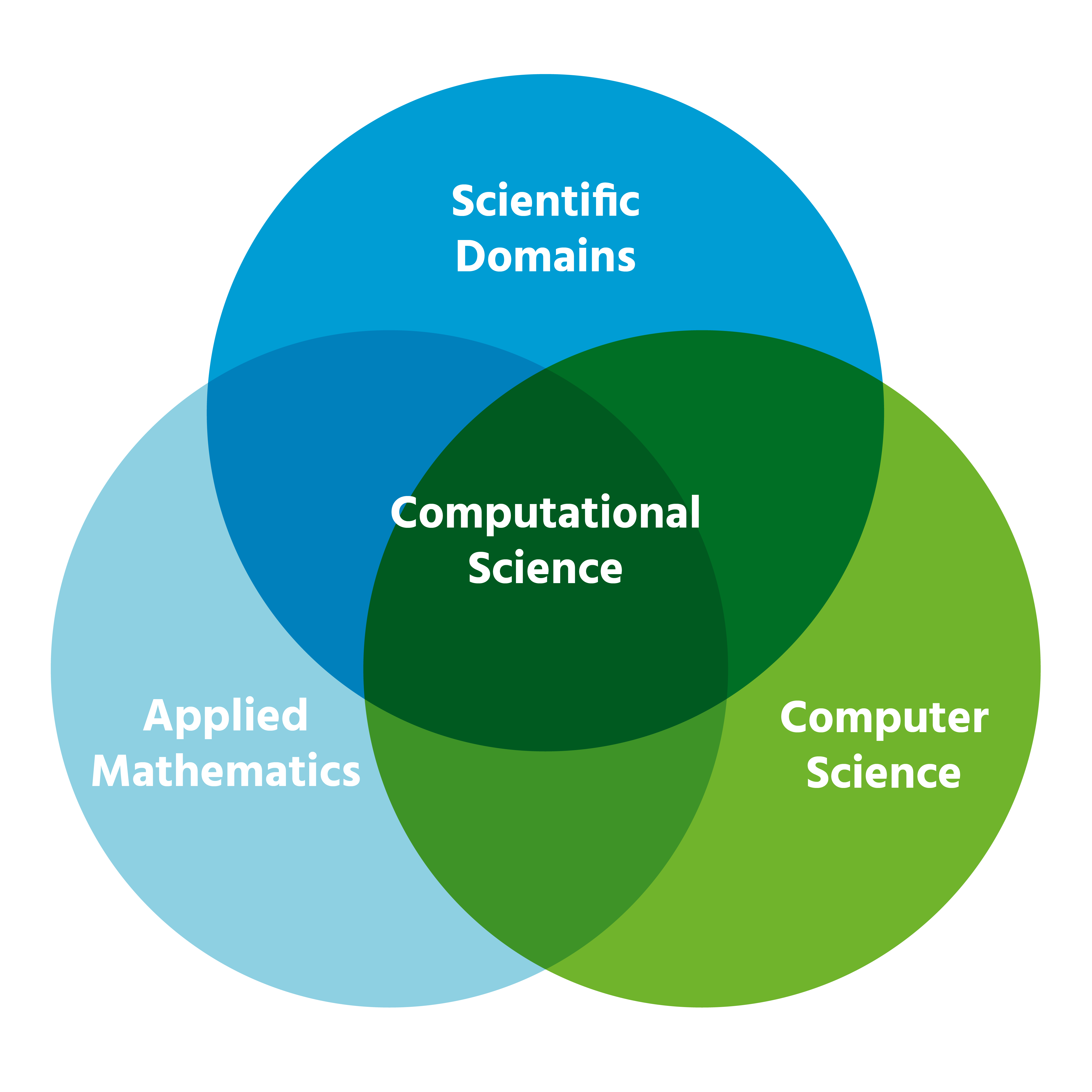
The Science That Combines Technology and Engineering
The science that explicitly combines technology and engineering is typically called applied engineering or engineering science . These disciplines integrate scientific theory, engineering principles, and technological innovation to design, build, and improve products, services, and systems [3] . Applied engineering, in particular, focuses on the practical implementation of both existing and emerging technologies in real-world settings.
Examples include:

Source: tunesloaded.com.ng
- Bioengineering : Merges biological science, technology, and engineering to develop medical devices and treatments.
- Chemical engineering : Applies chemistry and engineering to transform raw materials into valuable products.
- Civil engineering : Combines physics, materials science, and technological tools to build infrastructure.
Each of these fields is rooted in applied science and demonstrates the synergy of technology and engineering in creating solutions that impact society [4] .
How Applied Science Differs from Pure Science
Understanding the distinction between pure (basic) science and applied science is essential for anyone considering a career in these areas. Pure science seeks to expand knowledge for its own sake, focusing on theories, principles, and explanations of natural phenomena. Applied science , on the other hand, is about using that knowledge to create solutions, products, or systems that address actual needs [5] .
For example, a pure scientist may study the properties of a new material, while an applied scientist will use that information to design stronger buildings or more efficient electronics. This practical orientation makes applied science highly relevant to industries seeking innovation and efficiency.
Real-World Examples of Applied Science in Action
Applied science is all around us. Some prominent examples include:
- Healthcare : Development of vaccines, medical imaging devices, and prosthetics.
- Environmental engineering : Creation of water purification systems and renewable energy technologies.
- Information technology : Implementation of cybersecurity protocols and data analysis tools.
Each of these innovations began with scientific discovery and was brought to life through applied science, technology, and engineering [4] .

Source: alertageekchile.cl
Paths to a Career in Applied Science
If you are interested in pursuing a career in applied science or a related field, there are several actionable steps you can take:
- Identify your area of interest : Applied science covers a wide range of industries, including engineering, healthcare, environmental science, and technology. Consider which sector aligns with your skills and passions.
- Pursue relevant education : Most careers require at least an associate or bachelor’s degree in a relevant field. For example, an Associate of Applied Science (AAS) or a Bachelor of Applied Science (BAS) can lay the foundation for technical roles [1] .
- Gain practical experience : Internships, co-op programs, and entry-level positions provide hands-on learning and help you build a network in your chosen field.
- Earn certifications : Many technical roles value industry certifications, which demonstrate specific skills and knowledge. Research which credentials are most respected in your area of interest.
- Stay current : Applied science is always evolving. Follow industry news, attend workshops, and participate in professional organizations to stay ahead.
To find accredited programs, you can search for degree options at local universities or community colleges. If you are interested in specific careers, consider contacting professional associations such as the American Society for Engineering Education or the National Society of Professional Engineers for guidance on recognized pathways and resources.
Applying for Programs and Opportunities
While many institutions offer programs in applied science, engineering, and technology, requirements and processes vary. Here is how you can get started:
- Research accredited colleges or universities that offer Associate of Applied Science or Bachelor of Applied Science degrees. Use official college search portals or visit the website of your preferred institution.
- Contact the admissions office for application requirements, deadlines, and financial aid options. They can provide guidance on prerequisites and scholarship opportunities.
- If you are interested in technical certifications or professional development, search for programs recognized by industry bodies in your field. For example, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers offers various credentials for engineering professionals.
- Consider attending open houses, webinars, or virtual tours offered by educational institutions to gain a better understanding of their applied science programs.
If you are unsure where to start, you may contact your local community college or search for “applied science programs” to find opportunities near you. Many institutions have advisors who can help map out a personalized pathway based on your background and goals.
Challenges and Solutions in Applied Science Careers
Like any field, careers in applied science come with unique challenges:
- Keeping up with rapid technological change : Continuous learning is essential. Professional development courses and industry events can help you stay updated.
- Balancing theory and practice : Applied science requires both deep theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Seek out programs and employers that value hands-on experience.
- Finding the right specialization : With so many branches, it can be difficult to choose a focus. Speak with mentors, join professional organizations, and participate in internships to explore your options.
Despite these challenges, the rewards are significant. Applied science professionals are in demand across industries, and the work directly contributes to solving real-world problems.
Alternative Approaches and Expanding Opportunities
Applied science is not limited to traditional engineering or technology roles. Many interdisciplinary fields now integrate applied science with business, policy, and design. Examples include:
- Data science : Uses statistical and computational techniques to solve industry-specific problems.
- Environmental technology : Applies scientific methods to develop sustainable solutions for ecological challenges.
- Healthcare technology : Combines biomedical research, engineering, and information technology to improve patient care.
To explore these emerging opportunities, consider connecting with professional groups, attending career expos, or participating in online forums dedicated to your area of interest.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Applied science-sometimes called practical science, engineering science, or simply technology-is the engine driving innovation by uniting scientific knowledge with real-world application. The science that most directly combines technology and engineering is known as applied engineering or engineering science, and it spans a wide array of industries and career pathways. Whether you are a student, a career-changer, or an industry professional, there are accessible steps to begin or advance your journey in applied science. Stay curious, seek practical experience, and connect with experts to find your place in this ever-evolving field.
References
- International Student (2025). Study Applied Sciences in the US.
- Fiveable (2025). Applied science – Definition and Explanations.
- Wikipedia (2024). Outline of Applied Science.
- Indeed (2025). 10 Types of Applied Sciences: Career Paths and Benefits.
- Australian Swiss International School (2024). What is the Applied Sciences approach? A simple guide.
MORE FROM searchhole.com